
ALARM WATCH: A watch provided with the movement capable of releasing an acoustic sound at the time set. A second crown is dedicated to the winding, setting, and release of the striking-work; an additional center hand indicates the time set. The section of the movement dedicated to the alarm device is made up by a series of wheels linked with the barrel, an escapement and a hammer striking a gong or bell. This kind of timepiece works much like a normal alarm clock.
ANALOG or ANALOGUE: A watch displaying time indicators by means of hands.
ANTIREFLECTION, ANTIREFLECTIVE: Superficial glass treatment assuring the dispersion of reflective light. Better results are obtained if both sides are treated, but in order to avoid scratches no the upper layer, the treatment of the inner surface is preferred.
ARBOR: Bearing element of gear or balance, whose ends– called pivots– run in jewel holes or brass bushings.
AUTOMATIC: A watch whose mechanical movement is wound automatically. A rotor makes short oscillations due to the movement of the wrist. Through a series of gears, oscillations transmit motion to the barre, thus winding the mainspring progressively.
AUTOMATON: Figures placed on the dial or case of watches, provided with parts of the body or other elements moving at the same time as the sonnerie strikes. The moving parts are linked through an aperture on the dial or case back with the sonnerie hammers striking a gong.
BALANCE: Oscillating device that together, with the balance of the spring, makes up the movement’s heart as its oscillations determine the frequency of its function and precision.

BALANCE SPRING: Component of the regulating organ that together with the balance determines the movement’s precision. The material used is mostly a steel alloy. In order to prevent the system’s center of gravity from continuous shifts, it differs in rate according to the watches position. Thanks to the quality of materials today, it’s possible to assure an excellent precision of movement working even with a flat spring.
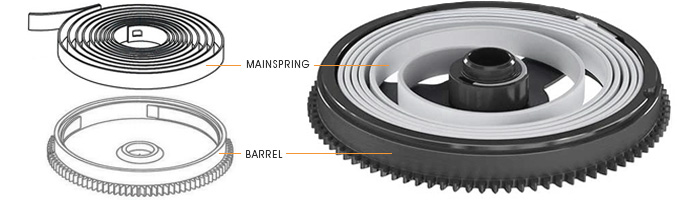
BARREL: Component of the movement containing the mainspring whose toothed rim meshes with the pinion of the first gear of the train. Due to the fact that the makeup of the barrel and mainspring transmits motive force, it is also considered to be the very motor. Inside the barrel, the mainspring is wound around an arbor turned by the winding crown, or in the case of the automatic movements, by the gear powered by the rotor.
BEVELING: Chamfering of edges, levers, bridges and other elements of a movement by 45 degrees. This is typically found in high-grade movements.
BEZEL: Top part of the case, sometimes holds the crystal. It may also be integrated with the case middle or a separate. element. It is snapped or screwed onto the middle.

BRACELET: A metal band attached to the case. It is called integral if there is no apparent discontinuity between the case and the bracelet. The profile of attachments is similar to the first link

BRIDGE: Structural metal element of a movement– sometimes called a cock or bar– supporting the wheel train balance escapement and barrel. Each bridge is fastened to the plate by means of screws and is locked into a specific position by pins. In high-quality movements, the sight surface is finished with various types of decoration.
BRUSHED, BRUSHING: Topical finish giving metals a subtle lined texture.
CABOCHON: Any kind of precious stone, polished but uncut. Generally, half a spherical shape mainly used as an ornament of the winding crown or certain elements of the case.

CALENDAR ANNUAL: An intermediate complication between a simple calendar and a perpetual calendar. This feature displays all the months with 30 or 31 days correctly but needs a manual correction at the end of February. Generally, date, day of the week and month, or only day and month are displayed on the dial.
CALENDAR FULL: Displaying date, day of the week, and month on the dial, but needing a manual correction at the end of a month with less than 31 days. It is often combined with the moon phase element.
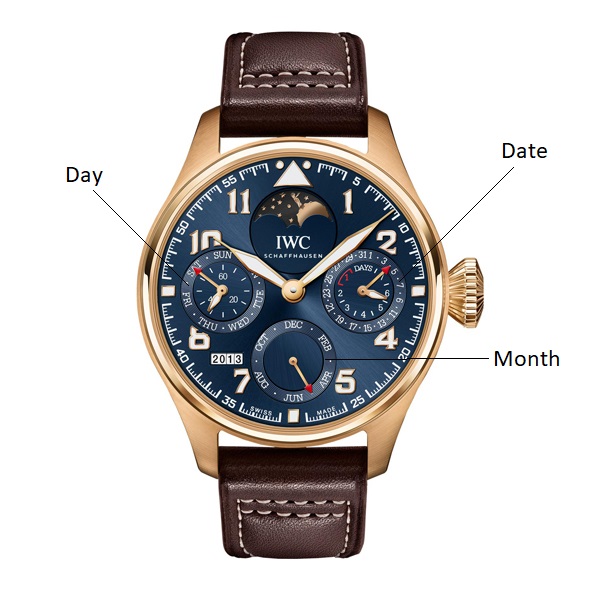

CALENDAR PERPETUAL: Describes a mechanism that correctly showcases the date on the watch “perpetually,” taking into account the different lengths of the month as well as leap days. The internal mechanism moves the dial to the next day.
CALIBER: Originally, it indicated only the size of a movement, but now the indication defines a specific movement type and shape. It’s combined with the constructor’s name and identification number. Therefore, the caliber identifies the movement.
CARRIAGE or TOURBILLON CARRIAGE: The rotating frame of a tourbillon device, carrying the balance and escapement. This is essential for a perfect balance of the whole system and its stability, in spite of its reduced weight. Because of the widespread use of the transparent dials, carriages became elements of aesthetic attractiveness.
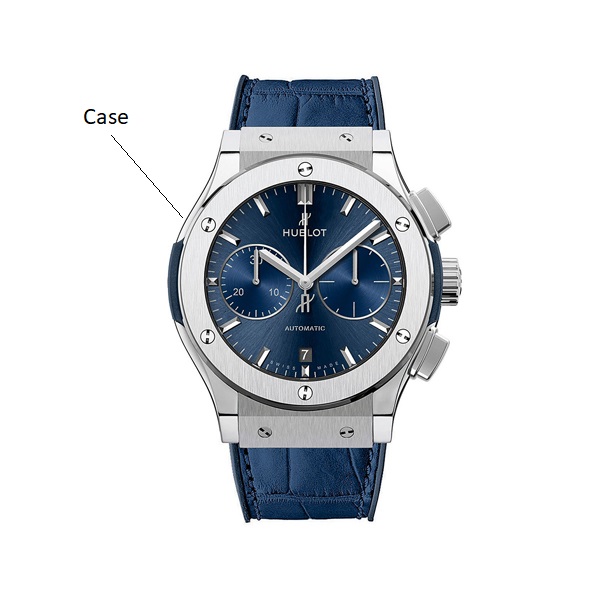
CASE: Container housing and protecting the movement, usually made up of three parts: middle, bezel and back.

CENTER SECOND HAND: Sweep second hand. [Refer to image featured in “Sweep Second Hand.”
CHAMPLEVE: Hand-made treatment of the dial or case surface. The pattern is obtained by hollowing a metal sheet with a graver and subsequently filling the hollows with enamel.
CHRONOGRAPH: A watch that includes a built-in stopwatch function. i.e., a timer that can be started and stopped to time an event. There are many variations of the chronograph.

CHRONOMETER: A high-precision watch. According to Swiss law, a manufacturer may put the word “chronometer” on a model only after each individual piece has passed a series of tests and obtained a running bulletin and a chronometer certificate by an acknowledged Swiss control authority, such as COSC.
CIRCULAR GRAINING: Superficial decoration applied to bridges, rotors, and pillar-plates in the shape of numerous slightly superposed small grains obtained by using a plain cutter and abrasives. Also called pearlage or pearling.
CLOISONNE: A kind of enamel work — mainly used for the decoration of dials — in which the outlines of the drawing are formed by thin metal wires. The colored enamel fills the hollows formed in this way. After oven-firing, the surface is smoothed until the gold threads appear again.
CLOUS DE PARIS: Decoration of metal parts characterized by numerous small pyramids.

COLUMN WHEEL: Part of chronograph movements, governing the functions of various levers and parts of the chronograph operation, in the shape of a small-toothed steel cylinder It is controlled by pushers through levers that hold and release it. It is very precise and usually the preferred type of chronograph operation.

COMPLICATION: Additional function with respect to the manual-winding basic movement for the display of hours, minutes and seconds. Today, certain features, such as automatic winding or date are taken for granted, although they should be defined as complications. The main complications are moon phase, power reserve, GMT and full calendar. Further functions are performed by so-called great complications, such as split-second chronograph, perpetual calendar, tourbillon and minute repeater.
CORRECTOR: Pusher positioned on the case side that is normally actuated by a special tool for the quick setting of different indications, such as date, GMT, full or perpetual calendar.
COSC: Abbreviation of “Controle Officiel Suisse des Chronometres” the most important Swiss institution responsible for the functioning and precision testing of movements and chronometers. Tests are performed on each individual watch at different temperatures and in different positions before a functioning bulletin and a chronometer certificate can be issued. A maximum gap of a -4/+4 seconds per day is tolerated.

COTES CIRCULAIRES: Decoration of rotors and bridges of movements, whose pattern consists of a series of concentric ribs.

COTES DE GENEVE: Decoration applied mainly to high-quality movements, appearing as a series of parallel ribs. You can notice this decoration by looking for repeated cuts of a cutter that leaves thin stripes.
COUNTER: Additional hand on a chronograph, indicating the time elapsed since the beginning of the measuring. On modern watches, the second counter is placed at the center, while the minute and hour counters have off-centered hands in special zones, also referred to as subdials.
CROWN: Usually positioned on the case middle and allows winding, hand-setting, and often date or GMT hand setting. It is linked to the movement through the winding stem passing through a hole in the case. For waterproofing purposes, simple gaskets are used in water-resistant watches, while diving watches adopt screwing systems (screw-down crowns).

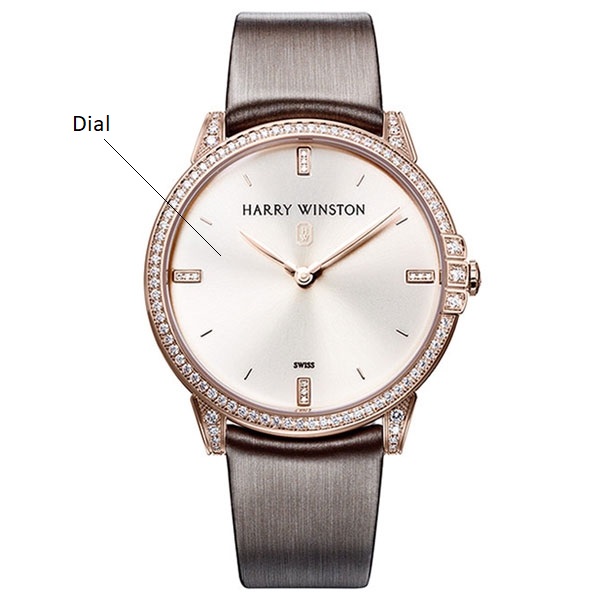
DIAL: Face of a watch, in which, the time and further functions are displayed. Dials can be made of gold, silver, brass and other materials.

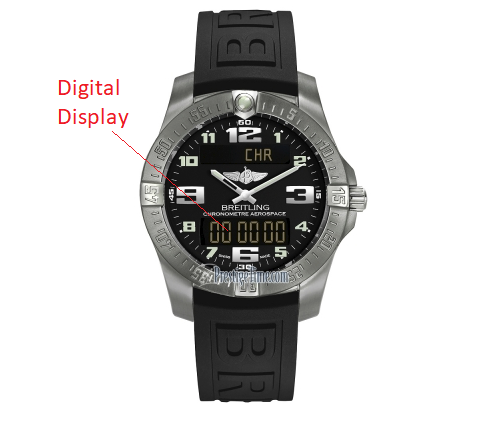
DIGITAL: Set of watches whose indications are displayed mostly inside an aperture or window on the dial.

ENDSTONE: Undrilled jewel placed on the balance jewel with the tip of the balance staff pivot resting against its flat surface, to reduce pivot friction. Also, it can be used for pallet staffs and escape wheels.
ENGINE-TURNED: Guilloche.
EQUATION OF TIME: Indication of the difference, expressed in minutes, between conventional mean time and real solar time. This difference varies from -16 to +16 seconds between one day and another.
ESCAPEMENT: Positioned between the train and the balance wheel, governing the rotation speed of the wheel-train wheels. The most widespread escapement type is the lever escapement.

FLINQUE: Engraving on the dial or case of a watch, covered with an enamel layer.
FLUTED: Surfaces worked with thin parallel grooves, mostly on dials or case bezels.

FLY-BACK: Feature combined with chronograph functions that allows a new measurement starting from zero by pressing down a second pusher, without stopping, zeroing and restating the entire mechanism. This function was initially developed to meet the needs of air forces.
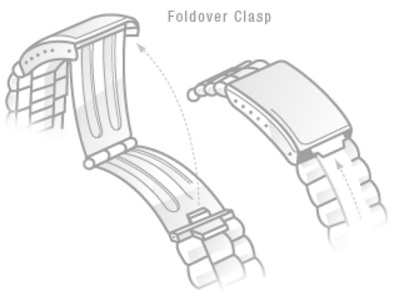
FOLD-OVER CLASP: Hinged and jointed element, normally the same material used for the case. Allows easy fastening of the bracelet on the wrist.
FREQUENCY: The number of cycles per time unit. For practical purposes, frequency is expressed in vibrations per hour (vph).
GENEVA SEAL: Poincon de Geneve.

GLUCYDUR: Bronze and beryllium alloy used for high-quality balances. This alloy assures high-elasticity and hardness values. It is antimagnetic, rustproof, and has a very reduced dilatation coefficient, which makes the balance very stable and assures high-accuracy of the movement.
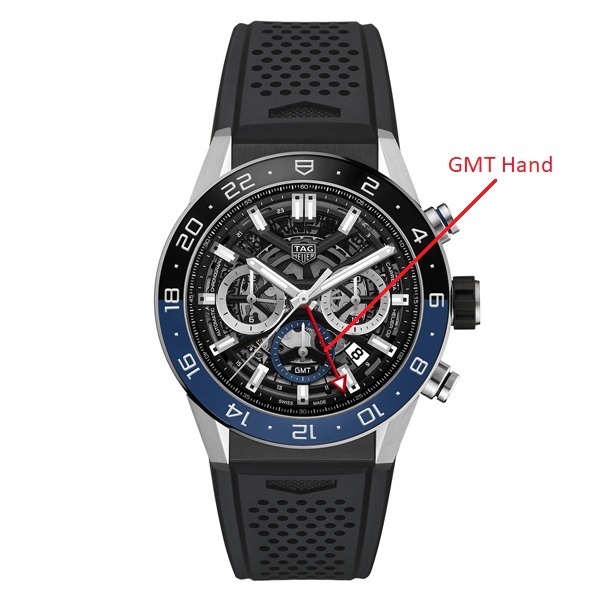
GMT: Abbreviation for Greenwich Mean Time. It means that two or more time zones are displayed.

GONG: Harmonic flattened bell in a steel alloy, generally positioned along the circumference of the movement and struck by hammers to indicate time by sounds.
GUILLOCHE: Decoration of dials, rotors or case parts consisting of patterns made by hand or engine-turned. Dials and rotors decorated this way are generally in gold or silver. [Refer to image featured in “Engine-Turned.”]
HAMMER: Steel or brass element used in movements provided with a repeater or alarm sonnerie. It strikes a gong or bell.
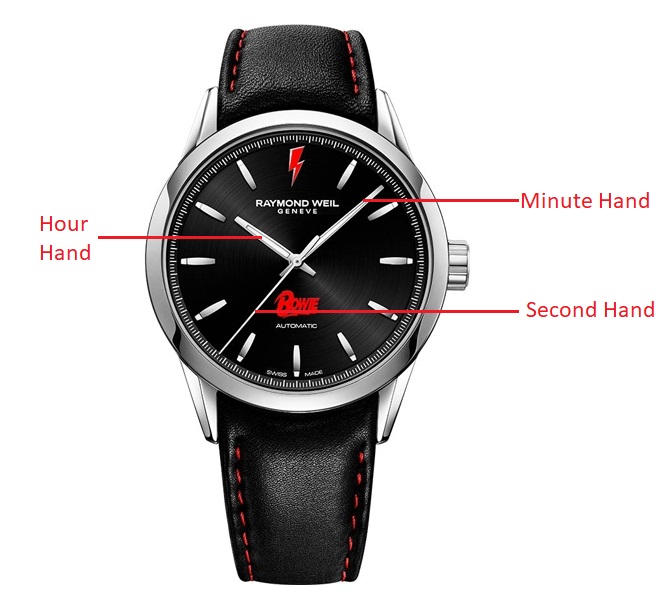
HAND: Indicator for the visualization of hours, minutes, and seconds as well as other functions. Normally, made of brass (rhodium-plated, gilded or treated otherwise) but also steel or gold.

HEART-PIECE: Heart-shaped cam generally used to realign the hands of chronograph counters.
HELIUM VALVE: Valve inserter in the case of some professional diving watches to discharge the helium contained in the air mixture inhaled by divers.

HEXALITE: An artificial glass made of a plastic resin.
INCABLOC: Shockproof.
JEWEL: Precious stone used in movements as a bearing surface. The steel pivots of wheels in movements turn inside synthetic jewels (mostly rubies) lubricated with a drop of oil. The jewels hardness reduces wear to a minimum even over long periods of time.

JUMPING HOUR: Feature concerning the digital display of time in a window. The indication changes almost instantaneously at every hour.
LINE: Ancient French measuring unit maintained in horology to indicate the diameter of a movement.
LUBRICATION: To reduce friction caused by the running of wheels and other parts. There are points to be lubricated with specific low-density oils.
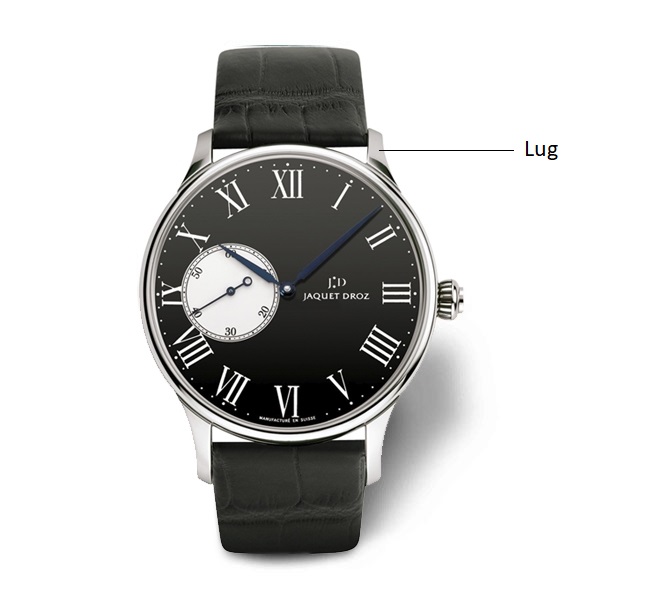
LUG: Double extension of the case middle by which a strap or bracelet is attached.

LUMINESCENT: Materials applied on markers and/or hands. Emitting the luminous energy previously absorbed as electromagnetic light rays.

MAINSPRING: This and the barrel make up the driving element of a movement. It stores and transmits the power force needed for its function.
MANUAL: A mechanical movement in which winding is performed by hand.
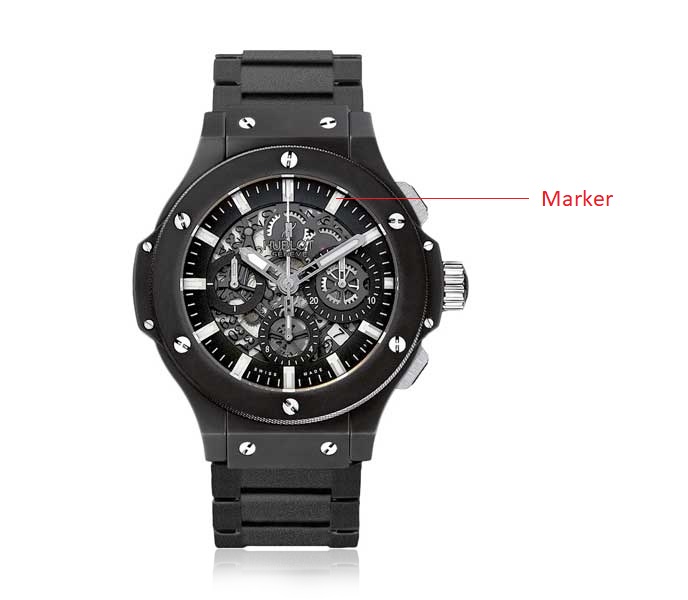
MARKERS: Elements printed or applied on the dial, used as reference points for the hands to indicate hours and fifteen or five-minute intervals.

MICROMETER SCREW: Element positioned on the regulator, allowing to shift it by minimal and perfectly gauged ranges so as to obtain accurate regulations of the movement.
MICRO-ROTOR: Roto
MINUTE REPEATER: Repeater.
MODULE: Self-contained mechanism, independent of the basic caliber, added to the movement to make an additional function available: chronograph, power reserve, GMT, perpetual or full calendar.
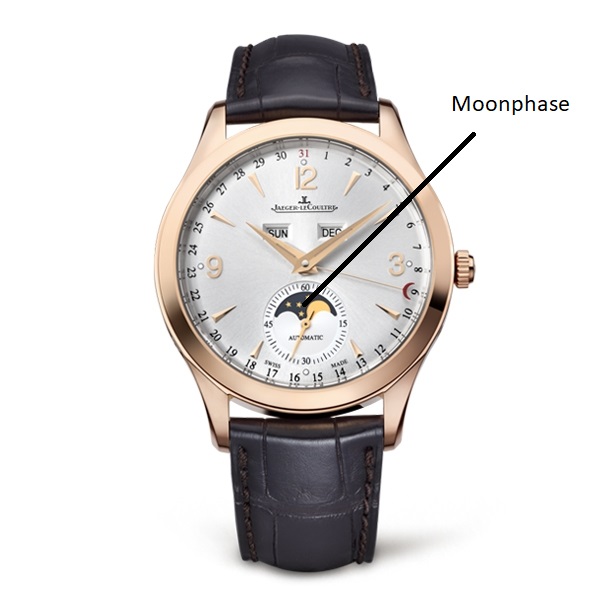
MOONPHASE: A function available usually combined with calendar-related features. The moon phase disc advances one tooth every 24 hours.

MOVEMENT: The entire mechanism of a watch. Movements are divided into two great families: quartz and mechanical; the latter are available with manual or automatic winding devices.

NIVAROX: Trade name (from the producer’s name) of a steel alloy, resisting magnetization used for modern self-compensating balance springs.
OSCILLATION: Complete oscillation or rotation movement of the balance, formed by two vibrations.
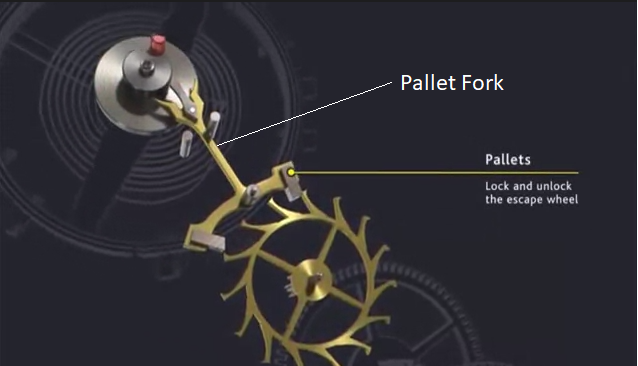
PALLET FORK: Device of the escapement that transmits part of the motive force to the balance wheel in order to maintain the amplitude of oscillations unchanged by freeing a tooth of the escape wheel at one time.
PILLAR-PLATE or MAIN-PLATE: Supporting element of bridges and other parts of a movement.
PINION: Combines with a wheel and an arbor to form a gear. A pinion has less teeth than a wheel and transmits motive force to a wheel. Pinion teeth are highly-polished to reduce friction to a minimum.
PIVOT: End of an arbor turning on a jewel support. Pivots are particularly thin and fragile, therefore they are protected by a shockproof system.
PLATED: Metal treated by a galvanized procedure in order to apply a slight layer of gold or another precious metal on a brass or steel base.
PLEXIGLAS: A synthetic resin used for watch crystal.
POINCON DE GENEVE: Distinction assigned by the Canton of Geneva to movements produced by watchmaker firms of the Region and complying with all the standards of high horology with respect to craftsmanship, small scale production, working quality, accurate assembly, and setting. The Geneva Seal is engraved on at least one bridge and shows the Canton’s symbol. For example, a two-field shield with and eagle and a key respectively in each field.

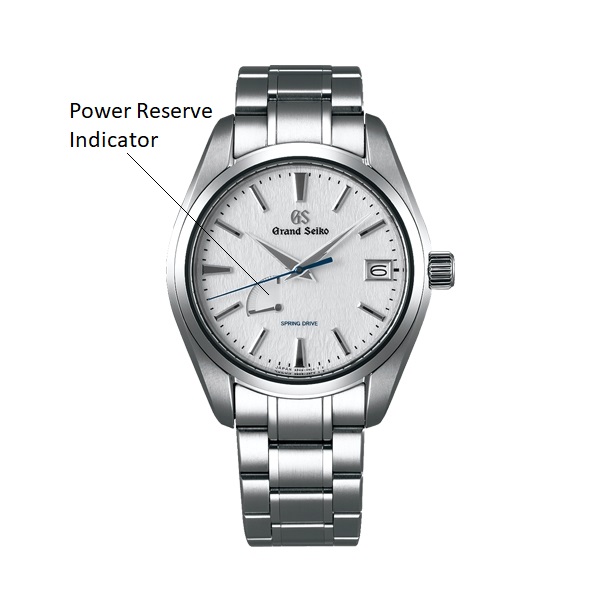
POWER RESERVE: Duration (in hours) of the residual functioning autonomy of a movement after it has reached the winding peak. The duration value is displayed by an indicator: analog (hand on a sector) or digital (through a window).

PULSOMETER CHRONOGRAPH: The pulsimeter scale shows the number of pulse beats per minute.
PUSHER, PUSH-PIECE or PUSH-BUTTON: Mechanical element mounted on a case for the control of specific functions. Usually used in chronographs, but also with other functions.

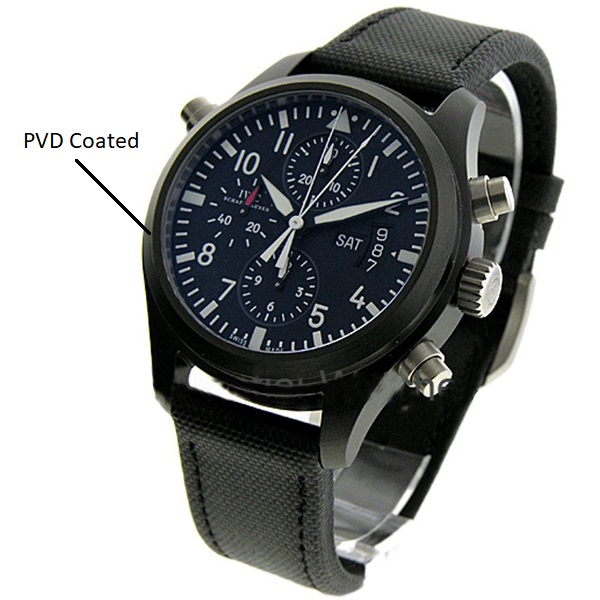
PVD: Abbreviation of Physical Vapor Deposition. A plating process, consisting of the physical transfer of substance by bombardment of electrons.

REGULATING UNIT: Made up by balance and balance spring, governing the division of time within the mechanical movement, assuring its regular running and accuracy.
REGULATOR: Regulating the function of a movement by lengthening and shortening the active section of the balance spring.

REPEATER: Mechanism indicating time by acoustic sounds. Repeaters work on demand by actuating a slide or pusher, positioned on the case side. Repeaters are normally provided with two hammers and two gongs. One for the minutes and one for the hours. The mechanism of the striking work is among the most complex complications.
RETROGRADE: A hand that, instead of making a revolution of 360 degrees before starting a new measurement, moves on an arc scale and at the end of its trip comes back instantaneously.
ROTOR: In automatic-winding mechanical movements the rotor is the part that, by its complete or partial revolutions, as well as the human arm, allows the winding of the mainspring. [Refer to image featured in “Micro-Rotor.”]
SCALE: Graduation on a measuring instrument, showing the divisions of a whole of values, especially on a dial or bezel. Scales used in horology, typically relate to the following measuring devices: tachometer, telemeter, and pulsometer.
SECOND TIME-ZONE INDICATOR: GMT and World Time.
SECTOR: Rotor. [Refer to image featured in “Micro-Rotor.”]
SELF-WINDING: Automatic.
SHOCKPROOF or SHOCK RESISTANT: Watches provided with shock-absorber systems (e.g. Incabloc) that help prevent damage from shocks to the balance pivots.
SKELETON or SKELETONIZED: Watches whose bridges and pillar-plates are cut out in a decorative manner, thus revealing all the parts of the movement.

SMALL SECOND: Time display in which the second hand is placed in a small subdial.

SNAILING: Decoration with a spiral pattern, mainly used on the barrel wheel or on big-sized full wheels.
SONNERIE (EN-PASSANT): Function consisting of an acoustic sound, obtained by a striking work made up of two hammers striking gongs at set hours, quarters and half hours.
SPLIT-SECOND CHRONOGRAPH: An additional hand is superimposed on the chronograph hand. Pressure on the pusher starts both hands, which remain superimposed as long as the split second mechanism is not blocked. After recording, the same pusher is pressed a second time, releasing the split-second hand, which instantly joins the still-moving chronograph hand. Thus, synchronizing with it to prepare for another recording. This type of function is particularly useful for timing simultaneous phenomena which began at the same time, but end at different times.

STAFF or STEM: Arbor.
STRIKING WORK: Sonnerie and Repeater.
SUBDIAL: Zone. [Refer to inage featured in “Zone.”]
SUPER-LUMINOVA: Luminsecent. [Refer to image featured on “Luminsecent.”]
SWEEP SECOND HAND: A center second hand mounted on the center of the main dial.
TACHOMETER or TACHYMETER: Function measuring the speed at which the wearer runs over a given distance. The tachometer scale is calibrated to show the speed of a moving object. The figure indicated by the hand on the tachometer scale represents the speed in kilometers or miles per hour.
TELEMETER: By means os a telemeter scale, it is possible to measure the distance of a phenomenon that is both visible and audible.
TONNEAU: The particular shape of a watch caste, imitating the profile of a barrel. For example, straight shorter horizontal lines and curved, longer vertical sides.

TOURBILLON: Device invented in 1801 by A.L. Breguet. This function equalizes position errors due to changing positions of a watch and related effects of gravity. Balance, balance spring and escapement are housed inside a carriage. Also called a cage, rotating by one revolution per minute. This compensates for all the possible errors over 360 degrees.
VIBRATION: Movement of a pendulum or other oscillating bodies, limited by two consecutive extreme positions.
WATER RESISTANT or WATERPROOF: A watch whose case is designed to resist infiltration by water (3 atmospheres, corresponding to a conventional depth of 30 meters; 5 atmospheres, corresponding to a conventional depth of 50 meters.)
WHEEL: Circular element, mostly toothed, combines with an arbor and a pinion to make up a gear.
WINDING STEM: Element that transmits motion from the crown to the gears governing manual winding and setting. [Refer to the image featured in “Stem.”]
WINDOW: aperture in the dial that allows reading the indication shown, mainly the date but also other underlying indications.
WORLD TIME: Additional feature provided with a GMT function, displaying the 24 time zones on the dial or bezel, each referenced by a city name, providing an instant reading of the time of any country.

Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest updates and releases
Thank you for subscribing to your newsletter. We’ll keep you posted on the latest news and updates with King Jewelers.
 You ‘ve been added to our mailing list
You ‘ve been added to our mailing list
Based on your recently viewed products
Enter your email address below, and if an account exists, we’ll send you a link to reset your password.
Need help with your ring size? Read our article here. Don't see your size? Contact us!
Add to bagNeed help with your ring size? Read our article here. Don't see your size? Contact us!
Add to favorites